- Carotid ultrasound
- Doppler ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- Computerized tomography angiography (CTA)
- Cerebral angiography, or carotid angiogram
With the exception of the carotid angiogram, these are noninvasive tests that allow the doctor to see narrowing and blockages of the carotid arteries. In some cases, they can see that a stroke is imminent. Discuss your diagnostic options with your doctor at Maryland Vascular Specialists.
{,}show_first{:}{|}tab_name{:}How Is It Treated?{,}tab_content{:}If you have early signs of carotid artery disease, these are some preventive steps you can take to prevent the risk of stroke:
- Start a smoking cessation plan, if you smoke
- Work on losing weight, if you are overweight/obese
- Limit alcohol, cholesterol, fat, and salt in your diet
- Exercise regularly
- Take any medications suggested by your doctor
Your doctor may recommend medications like aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), or warfarin (Coumadin) to help control your condition. There are also medical procedures to treat carotid artery disease, including:
- Carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
- Carotid artery stenting (CAS)
Remember, carotid artery disease can be a “silent killer” with no symptoms until a life-threatening stroke. To put your mind at ease, schedule a consultation with Maryland Vascular Specialists.
{,}show_first{:} )Carotid Artery Disease – Symptoms, Risks, Treatment
Carotid Artery Disease – Symptoms, Risks, Treatment
When the carotid arteries are blocked, you are at an increased risk of stroke, which is the 5th leading cause of death in the United States. Unfortunately, people with carotid artery disease often don’t even realize they have it.
Here’s a look at the risk factors, along with common symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment procedures that you may experience at Maryland Vascular Specialists.
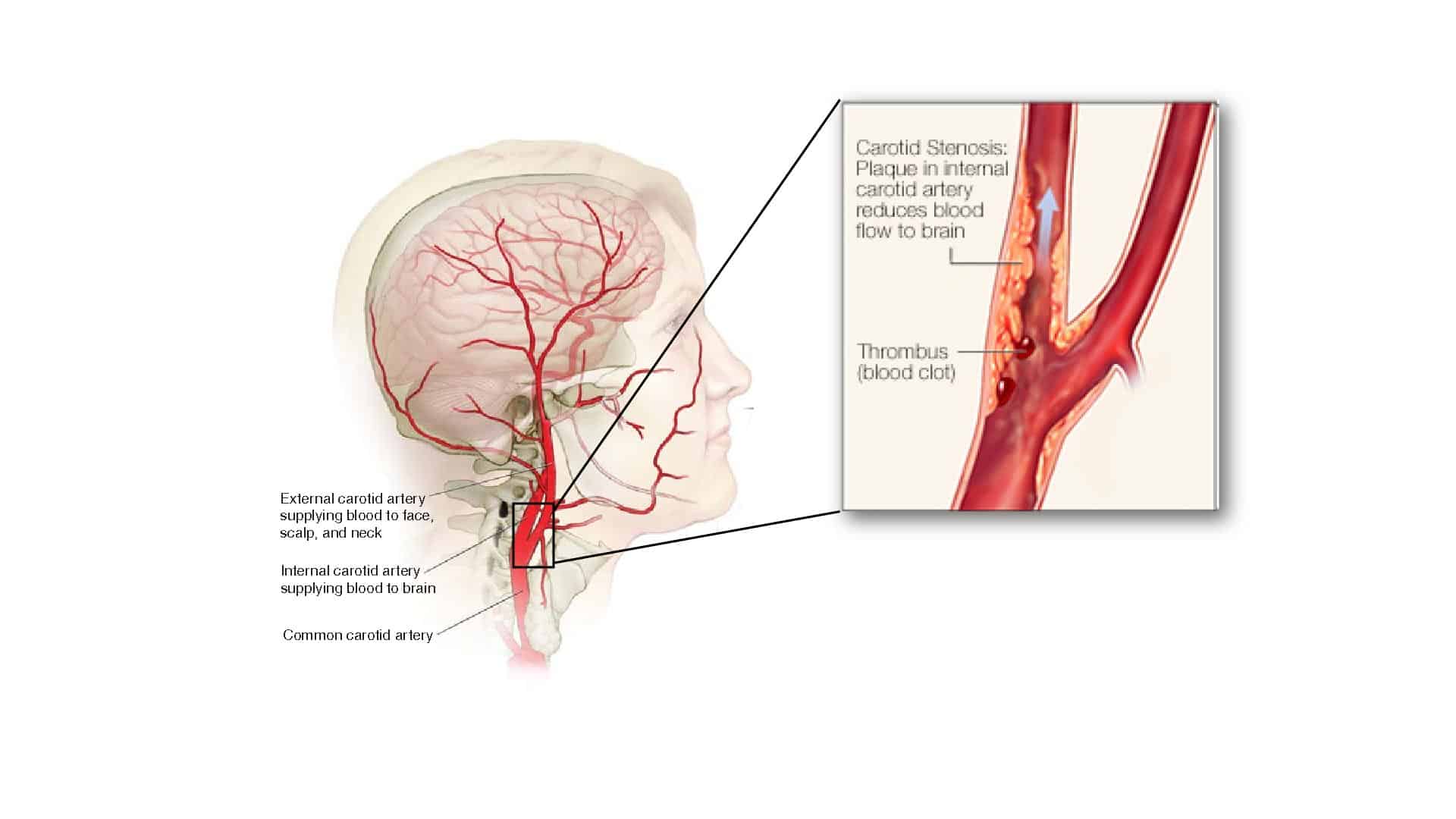
Overview Of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid Artery Disease, also known as carotid artery stenosis, refers to a condition where the carotid arteries narrow due to the buildup of deposits. The carotid arteries are located on either side of your neck and supply blood to the scalp, face, neck, and brain.
The narrowing that occurs is a result of fatty substances and cholesterol deposits that settle into a thick plaque along the artery passageways. If occlusion, or total blockage, occurs, the person will be in a life-threatening medical situation.
There are more than 700,000 strokes each year in the U.S. and carotid artery disease is one of the most important and preventable causes.
Symptoms Of Carotid Artery Disease
Over time, as substances begin to build up and form a plaque on the arterial wall, the person may feel no outward symptoms. Their body copes with the narrowed arteries and they continue feeling normal.
In fact, all of the following things can happen in early carotid artery disease without the patient being aware of them until a health emergency, like a stroke, happens:
- The artery becomes extremely narrowed
- A piece of plaque breaks off and travels to the smaller arteries of the brain
- A blood clot forms
- Blood vessels become obstructed
When the carotid arteries are blocked, you are at an increased risk of stroke, which is the 5th leading cause of death in the United States. Unfortunately, people often don’t even realize they have it.
Here’s a look at the risk factors and common symptoms, as well as along with common symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment procedures that you may experience at Maryland Vascular Specialists.
Causes Of Carotid Artery Disease
The cause of this disease is the buildup of fat and cholesterol in the arteries. Various factors come together to increase someone’s likelihood of having blocked arteries. These factors include genetics, lifestyle variation, and other contributing health conditions.
You are more likely to have the disease if you have diabetes, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure. Other contributors are being a smoker, being overweight, not getting much exercise, or not eating a healthy diet. Lifestyle factors aside, some people are simply more likely to get carotid artery disease due to the power of genetics.
To diagnose this disease, a doctor may listen for an abnormal sound called a bruit in the arteries of the neck. It is often described as a whooshing sound and is a sign of turbulent blood flow. Vascular specialists are trained to recognize it.
Other methods of diagnosis may include:
- Carotid ultrasound
- Doppler ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- Computerized tomography angiography (CTA)
- Cerebral angiography, or carotid angiogram
With the exception of the carotid angiogram, these are noninvasive tests that allow the doctor to see narrowing and blockages of the carotid arteries. In some cases, they can see that a stroke is imminent. Discuss your diagnostic options with your doctor at Maryland Vascular Specialists.
If you have early signs of carotid artery disease, these are some preventive steps you can take to prevent the risk of stroke:
- Start a smoking cessation plan, if you smoke
- Work on losing weight, if you are overweight/obese
- Limit alcohol, cholesterol, fat, and salt in your diet
- Exercise regularly
- Take any medications suggested by your doctor
Your doctor may recommend medications like aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), or warfarin (Coumadin) to help control your condition. There are also medical procedures to treat carotid artery disease, including:
- Carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
- Carotid artery stenting (CAS)
Remember, carotid artery disease can be a “silent killer” with no symptoms until a life-threatening stroke. To put your mind at ease, schedule a consultation with Maryland Vascular Specialists.